- Published on
Color Science 101
- Authors

- Name
- Garfield Zhu
- @_AlohaYo_
@Author: Garfield Zhu
1. Color basic
What is color? How we describe color?
- Color display spectrum



The Human's retina contains three types of color receptors (called cone cells in vertebrates) with different absorption spectra.
We say S-cone, M-cone, L-cone, and they are activated by blue, green and red.
They just like filter for lights.
Color is a biological phenominon. Now that human has only three color filters for nature lights, it means that some different combinations of lights could result in the same received waves in human's brains.
It is like this:
Metamerism spectrum example sample

The color Purple (magenta) does not exist?
We see the color wave length is linear, increasing from blue to red. But there are some colors exist between blue and red. Why?
Theoretically, magenta between purple and red does not exist in nature color. It's a "imagine color" by our brain. It makes hue a ring.
Hue ring

See more in color space section.
Color is a biological phenominon. Now that human has only three color filters for nature lights, it means that some different combinations of lights could result in the same received waves in human's brains.
It is like this:
Metamerism spectrum example sample

The color Purple (magenta) does not exist?
We see the color wave length is linear, increasing from blue to red. But there are some colors exist between blue and red. Why?
Theoretically, magenta between purple and red does not exist in nature color. It's a "imagine color" by our brain. It makes hue a ring.
Hue ring

See more in color space section.
2. Color Vision
Color relativeness
Color is relative. Our eyes is simple to be cheated.
Is A and B same?

Now we hide the black and white blocks.

Color constancy
Is the strawberry is red?
NO! IT'S ACTUALLY GRAY!

3. Color Model
3.1 RGB
Red, Green, Blue.
Additive color (mixing)
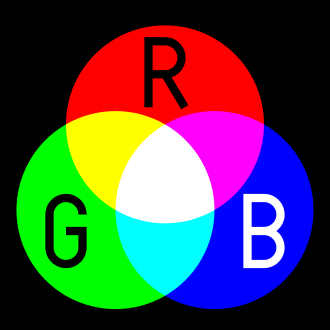
Additive color models are applied in the design and testing of electronic displays that are used to render realistic images containing diverse sets of color using phosphors that emit light of a limited set of primary colors.
3.2 CYMK
Cyan, Yellow, Magenta, blacK.

The more you mix, the darker it will be.
Widely used in printing.
Printing with CMYK pigments:

Subtractive color (mixing)
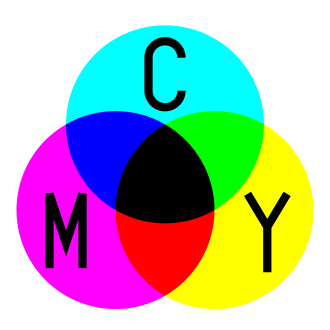
This idealized model is the essential principle of how dyes and inks are used in color printing and photography where the perception of color is elicited after white light passes through microscopic "stacks" of partially absorbing media allowing some wavelengths of light to reach the eye and not others.
Why black?
For cheapness. Mixing C, M, Y, we can get black. But in printing, we typically use black, always mixing CMY is too expensive and it introduces black in this system for a cheap printing for non colorful contents.
4. Color Space and Gamut
4.1 CIE 1931
CIE 1931 color space are the first defined quantitative links between distributions of wavelengths in the electromagnetic visible spectrum, and physiologically perceived colors in human color vision. The mathematical relationships that define these color spaces are essential tools for color management, important when dealing with color inks, illuminated displays, and recording devices such as digital cameras.
CIE 1931 RGB color matching functions

It describes the how to mix up the visible colors in different wave length using RGB, to match what human can see.
The negative value means that mixing RGB could not present the target color at postive values. Then we mix color to target color to match back the test color and we subtract the value added to target color from the tested one.
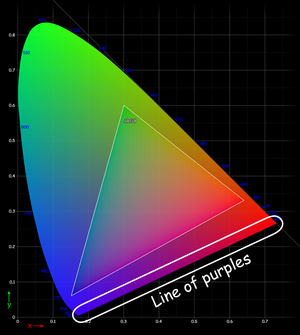
The CIE 1931 color space chromaticity diagram

4.2 Color Space
Reading color space
- Tooltips and wave length
Tooltips of reading colorspace graph:


- Line of purples
- White balance
Color temprature:

Hues of the Planckian locus on a linear scale (values in kelvin)

White & gold, or blue & black ?
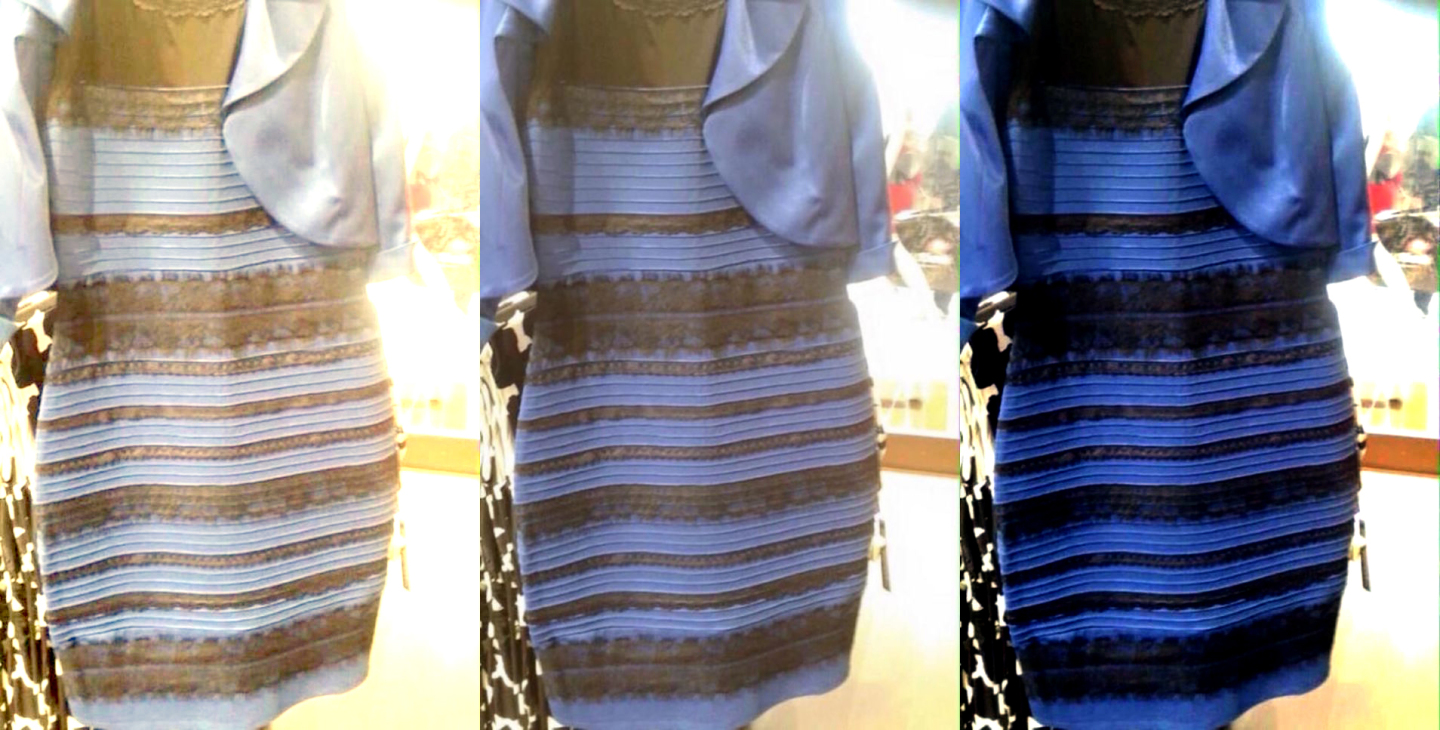

White balance:
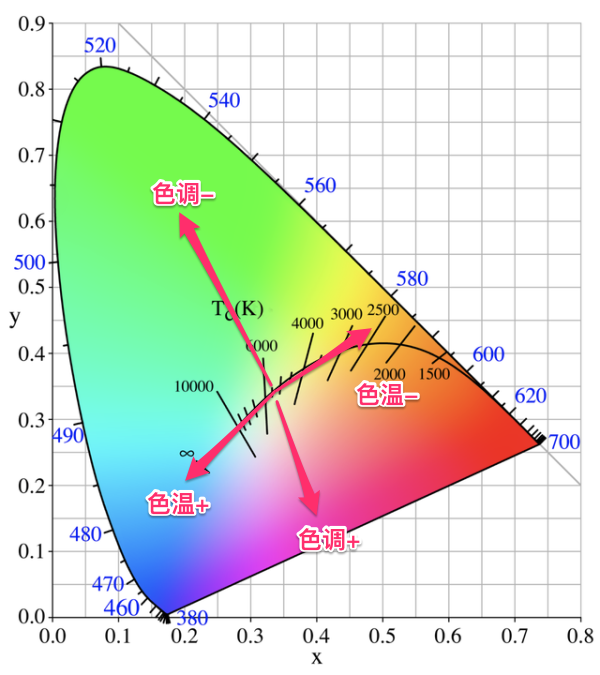
Adjust white balance requires two dimensions: temprature (for blue to yellow) and tint (from green to red)
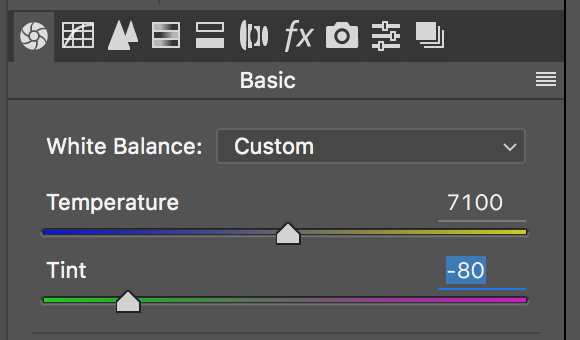
RGB
Define red, green and blue as orthogonal, we could have a cubic RGB space.
RGB cube space:

HSL/HSV
HSV cylinder:
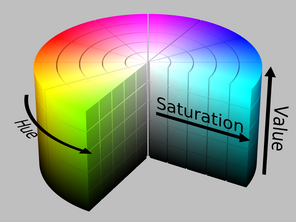
HSV cone:

a. Hue
The "kind" of color, regardless of attributes
Colorimetric correlate: dominant wavelength
Artist's correlate: the chosen pigment color
Newton's color circle & CSS hue ring:
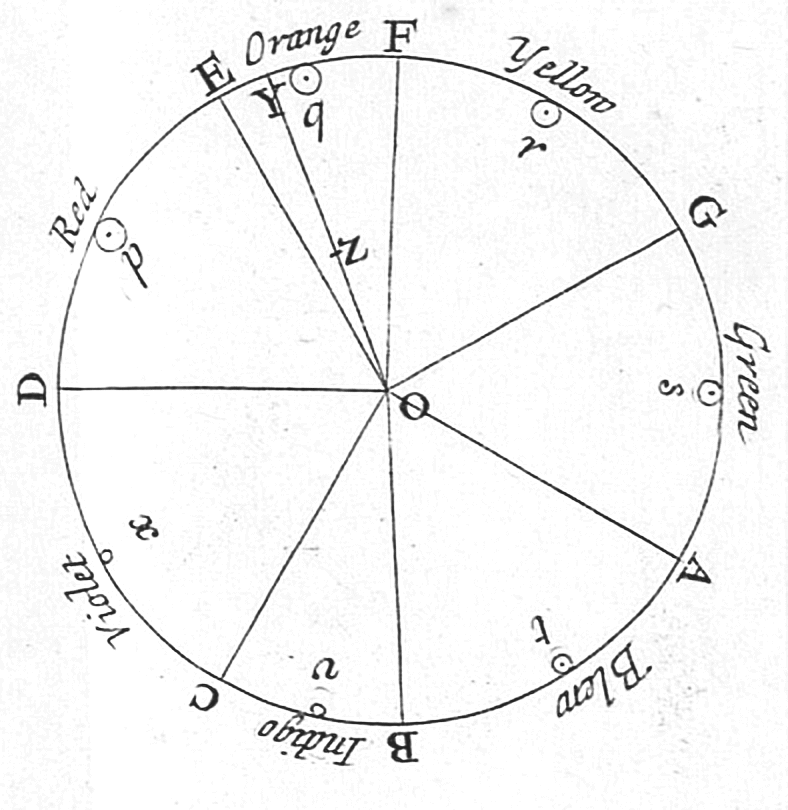

b. Saturation
- The "colorfulness"
- Colorimetric correlate: purity
- Artist's correlate: fraction of paint from the colored tube
c. Lightness (or value)
- The overall amount of light
- Colorimetric correlate: luminance
- Artist's correlate: tints are lighter, shades are darker
Common color pickers are based on HSV/HSL.
Color picker:

It is actually a section view of the cylinder.
Extension - Lipstick
4.3 Gamut
Gamut is the set of chromaticities generated by a set of color primaries,
Different color spaces represent different ranges of color.
Typically, we see four standards in consuming monitors: sRGB, DCI-P3, AdobeRGB, and NTSC.
Common gamuts:

sRGB sRBG, AKA standard RGB is the most widely adopted color space on computer today. HP and Microsoft created cooperatively in 1996 to use on monitors, printers, and the Web.
- Common moditor RGB standard. Other color devices simulate that monitor by calibration.
- Using 8-bit integer for R,G,B channels.
- Morden browser standard now support sRGB only.
- Gamut is limited. Tag "<canvas>" are discussed to support more wild gamut
NTSC Named after National Television System Committee. It's an old standard for TV.
- Old (1952), and for analog TV signals, not proper for digital monitor signals nowadays.
- Wide range, but not that accurate.
- 72% NTSC ≈ 100% sRGB
DCI-P3 Defined by the Digital Cinema Initiatives (DCI), expected to see adoption in television systems and in the home cinema domain.
- Morden (2010), wild, cinema industry usage.
- Uses a slightly warmer and greener whitepoint with a correlated color temperature of approximately 6300K
- Apple products: iPhone, Macbook, iPad, etc.
AdobeRGB Developed by Adobe Systems, Inc.
- Wide, Adobe products: PDF, PS, LR, PR, AE, etc.
- Improving upon the gamut of the sRGB color space, primarily in cyan-green hues.
- Printing standard. If you need a accurate printed color against what it shows on screen, AdobeRGB is necessary.
Gamut Coverage vs. Gamut volume
Gamut coverage is: the percentage of covered gamut area / the gamut area.
Gamut volume is: the percentage of the volume of the (device) supported colors / the volume of a gamut.
It means the "coverage" focuses on accuracy. The higher the coverage is, the more accurate of the device displaying the gamut. And the "volume" focuses on amount. The higher the volume is, the more color that device could display.
Color difference
Euclidean distance Just describe the color's distance in distance.
Formula:
Or, with weighting:
ΔE* (Delta-E) Human is not equally sensitive at different hue and lightness. Then CIE defines Delta-E for a more accurate color different.
Based on CIELAB color space.
More accurate for most people, widely adopted.
MacAdam ellipse defines a tolerance of color in different colors.
MacAdam ellipse (x10):

Color depth
Color depth, AKA bit depth, is the number of bits used to indicate the color of a single (sub)pixel.
When we say RGB in web, we say a 8-bit color depth for R,G,B channels (also say 24-bit true color), each of which ranges from 0~255. And for a single pixel, we have 2^8 * 2^8 * 2^8 = 2^24 ≈ 16 million colors.
In a scenario color changes gradiently in short range, bit depth makes a difference obviously.
Color banding will occur, when color depth is not deep enough with a dramatic color change:

8-bit vs. 10-bit:

- FRC,Frame Rate Control FRC is a form of temporal dithering which cycles between different color shades with each new frame to simulate an intermediate shade. Typically, physical 6-bit + FRC simulates a 8-bit, physical 8-bit + FRC simulates a 10-bit.
SP-4.4 Suggestion for buying a monitor
Resolution: 2k for 21', 23'/24', 27' monitors. 4k for 27', 32' monitors. 1080P not recommended, 8k is of low price–performance ratio. Larger size? Why not a TV.
Refresh rate: Theoeretically the higher, the better. High refresh rate is meaning for gaming (90Hz+), especially FPS (120Hz+) For movie and browser usage, 60Hz is enough anyway.
Panel: IPS, VA, TN. Just pick IPS.
HDR: HDR10, HDR400, HDR600, HDR1000. 10/400 is not recognizable. 600/1000 is very expensive. No necessary unless you have blue-ray HDR movies. If you need, better to have a HDR TV.
Gamut: (in product details/spec)
- NTSC is really outdated. Do not pick one if it only says its NTSC coverage (typically 72%).
- Confirm you are validting gamut coverage rather than volume. If one says gamut volume only but no coverage (typically 120%+ even 140%), DO NOT BUY IT! An extremely high volume is actually a disadvange which will make color not accurate. And guess why them don't say their coverage?
- 99% sRGB coverage is enough and for any common usage. It's a prerequisite for a higher persue.
- Pick a P3 if you uses Apple products. As monitor for iMac, Macbook, Mac mini, iPad, etc. 90%+ P3 is good, pick a 95%+ P3 at an acceptable price. Really comfortable (truct Apple),
- AdobeRGB coverage is always good, but expensive. Pay it for your interests on photographing and photo-printing.
Color difference: Delta-E <= 2 is far good enough for non-expert user. Smaller is better, but not necessary.
Color depth: see the color amount spec. 1.07 billion is worth of picking (Typically 8bit + FRC, real 10bit is more expensive). Be careful for 16 million colors, check if it tells a real 8bit or 6bit + FRC. If no obvious information as a real 8bit, not recommend unless a extreme high performance price ratio.
- Test a screen with testing patterns: https://www.eizo.be/monitor-test/